 |
| 1 . |
|
Click on the diagram to start the animation. What name is given to the process seen in this animation? (Activity: Making and Breaking Polymers)
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
Glycogen is _____. (Activity: Carbohydrates)
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
glucose + glucose —> _____ by _____. (Activity: Carbohydrates)
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
Which of these is a source of lactose? (Activity: Carbohydrates)
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
Which of these is a polysaccharide? (Activity: Carbohydrates)
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
_____ is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. (Activity: Carbohydrates)
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
Which of these is NOT a lipid? (Activity: Lipids)
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
This figure is an example of a(n) _____. (Activity: Lipids) 
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
Which of these is a phospholipid? (Activity: Lipids)
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
Which of these is rich in unsaturated fats? (Activity: Lipids)
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
A function of cholesterol that does not harm health is its role _____. (Activity: Lipids)
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
Click on the diagram to begin the animation. This animation illustrates the functioning of a _____ protein. (Activity: Protein Functions)
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
Arrow A is indicating a(n) _____ protein. (Activity: Protein Functions) 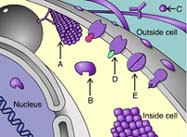
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
Arrow D is indicating a _____ protein. (Activity: Protein Functions) 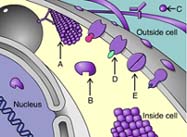
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
Which of these does NOT contain a structural protein? (Activity: Protein Functions)
|
 |
| 16 . |
|
Defensive proteins are manufactured by the _____ system. (Activity: Protein Functions)
|
 |
| 17 . |
|
Proteins are polymers of _____. (Activity: Protein Structure)
|
 |
| 18 . |
|
What type of bond joins the monomers in a protein's primary structure? (Activity: Protein Structure)
|
 |
| 19 . |
|
Which of these illustrates the secondary structure of a protein? (Activity: Protein Structure)
|
 |
| 20 . |
|
The secondary structure of a protein results from _____. (Activity: Protein Structure)
|
 |
| 21 . |
|
Tertiary structure is NOT directly dependent on _____. (Activity: Protein Structure)
|
 |
| 22 . |
|
If a strand of DNA has the nitrogen base sequence ATTTGC, what will be the sequence of the matching strand? (Activity: Nucleic Acid Structure)
|
 |
| 23 . |
|
If a DNA double helix is 100 nucleotide pairs long and contains 25 adenine bases, how many guanine bases does it contain? (Activity: Nucleic Acid Structure)
|
 |
| 24 . |
|
The two strands of a DNA double helix are held together by _____ that form between pairs of nitrogenous bases. (Activity: Nucleic Acid Structure)
|
 |
| 25 . |
|
A nucleotide is composed of a(n) _____. (Activity: Nucleic Acid Structure)
| | phosphate group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a hydrocarbon |
| | phosphate group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar |
| | glycerol, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar |
| | amino group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar |
| | sulfhydryl group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar |
|
 |
|