 |
| 1 . |
|
Based on the results of this cross, you determine that _____. (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over) 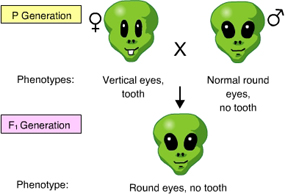
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
The results of the following cross indicate that the _____. (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over) 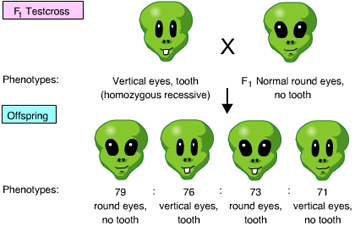
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
An F1 individual can produce _____ different gametes when both eye and tooth genes are considered. (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over) 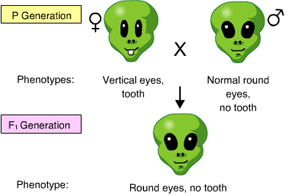
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
Given these chromosomes, which of the choices represents the possible recombinant gametes? (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over) 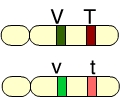
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
The results of a F1 testcross are: 250 bald head, four ears : 247 hairy head, six ears : 21 bald head, six ears : 19 hairy head, four ears. How many map units apart are the head and ear genes? (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over)
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
Which of the individuals is homozygous recessive for both of the gene pairs? (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over) 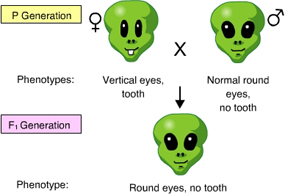
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
The results of the following cross indicates that the _____. (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over) 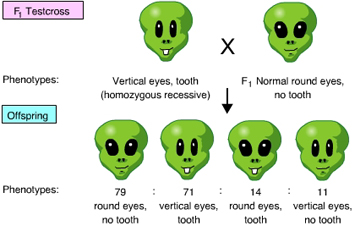
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
The recombination frequency between gene A and gene B is 8.4%, the recombination frequency between gene A and gene C is 6.8%, and the recombination frequency between gene B and gene C is 15.2%. Which of these is the correct arrangement of these genes? (Activity: Linked Genes and Crossing Over)
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
A color-blind woman mates with a male with normal color vision. Which of these results would indicate that color blindness is caused by an X-linked recessive allele? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind man has a daughter with normal color vision. What is the genotype of the daughter? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind man has a daughter with normal color vision. She mates with a male who has normal color vision. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind man has a daughter with normal color vision. She mates with a color-blind male. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A woman who is homozygous for normal color vision mates with a color-blind male. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind woman mates with a male with normal color vision. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. Under what conditions can an unaffected male have a color-blind daughter? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 16 . |
|
Hypophosphatemia (vitamin D-resistant rickets) is inherited as an X-linked dominant. An unaffected woman mates with a male with hypophosphatemia. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 17 . |
|
Hypophosphatemia (vitamin D-resistant rickets) is inherited as an X-linked dominant. A woman without hypophosphatemia and a man with hypophosphatemia have a daughter. The daughter mates with a male without hypophosphatemia. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 18 . |
|
Suppose that having three nostrils is a Y-linked character. A woman with two nostrils mates with a man with three nostrils. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity: Sex-Linked Genes)
|
 |
| 19 . |
|
Humans are diploid and have 46 chromosomes (or two sets). How many sets of chromosomes are found in each human gamete? (Activity: Polyploid Plants)
|
 |
| 20 . |
|
Humans are diploid and have 46 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are found in each human gamete? (Activity: Polyploid Plants)
|
 |
| 21 . |
|
_____ is the process by which haploid gametes form a diploid zygote. (Activity: Polyploid Plants)
|
 |
| 22 . |
|
A particular diploid plant species has 48 chromosomes, or two sets. A mutation occurs and gametes with 48 chromosomes are produced. If self-fertilization occurs, the gametes will have _____ set(s) of chromosomes. (Activity: Polyploid Plants)
|
 |
| 23 . |
|
Which of these terms applies to an organism with extra sets of chromosomes? (Activity: Polyploid Plants)
|
 |
| 24 . |
|
Mutant tetraploid plants _____. (Activity: Polyploid Plants)
|
 |
| 25 . |
|
Most polyploid plants arise as a result of _____. (Activity: Polyploid Plants)
|
 |
Answer choices in this exercise are randomized and will appear in a different order each time the page is loaded.
|