 |
| 1 . |
|
Ovules are found within structure _____. (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle) 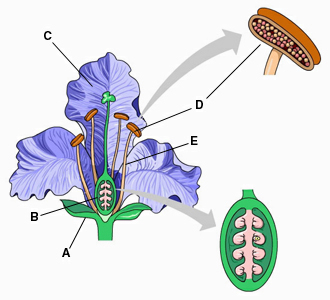
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
Which of these is unique to flowering plants? (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle)
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
The male gametophytes of flowering plants are also referred to as _____. (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle)
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
In flowering plants the integuments of the ovule develop into a(n) _____. (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle)
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
A carpel is composed of _____. (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle)
| | ovary, ovule, and anther |
| | ovule, megasporocyte, and anther |
| | zygote, anther, and endosperm |
| | stigma, style, and ovary |
| | petal, sepal, and stamen |
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
In flowering plants one megaspore gives rise to _____ nuclei. (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle)
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
A stamen consists of _____. (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle)
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
In angiosperms, pollination is the transfer of pollen grain to the _____ of a flower on the same plant or another plant of the same species. (Activity: Angiosperm Life Cycle)
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
What is endosperm? (Activity: Seed and Fruit Development)
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
The pointer is indicating a diploid cell that develops into the _____. (Activity: Seed and Fruit Development) 
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
Fruits evolved primarily as structures specialized to _____. (Activity: Seed and Fruit Development)
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
Why is golden rice pale yellow in color? (Activity: Seed and Fruit Development)
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
Which of these is a symptom of vitamin A deficiency? (Activity: Making Decisions About DNA Technology: Golden Rice)
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
Which of these is a vitamin A precursor? (Activity: Making Decisions About DNA Technology: Golden Rice)
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
The transfer of antibiotic-resistant genes from genetically engineered bacteria to disease-causing bacteria _____. (Activity: Making Decisions About DNA Technology: Golden Rice)
|
 |
|