 |
| 1 . |
|
The letter A indicates _____. (Activity: DNA Packing) 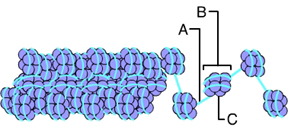
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
Where would RNA polymerase attach? (Activity: DNA Packing) 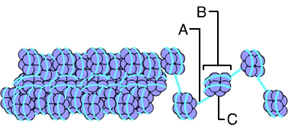
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
The letter C indicates _____. (Activity: DNA Packing) 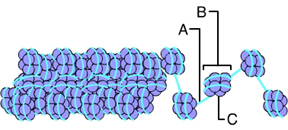
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
What is this an image of? (Activity: DNA Packing) 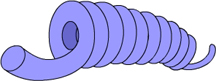
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
What is this an image of? (Activity: DNA Packing) 
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
Click on the diagram to begin the animation.
What name is given to this process? (Activity: Gene Amplification, Loss, and Rearrangement)
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
Rearrangement of the genome plays an important role in the _____ system. (Activity: Gene Amplification, Loss, and Rearrangement)
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
Which of these animations illustrates selective gene loss?
You will need to click on each choice to view the animation. (Activity: Gene Amplification, Loss, and Rearrangement)
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
The process of transcription is indicated by the letter _____. (Activity: Overview: Control of Gene Expression) 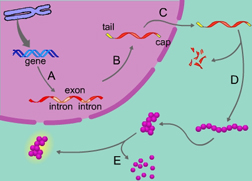
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
The letter E is indicating a process of gene expression that involves _____. (Activity: Overview: Control of Gene Expression) 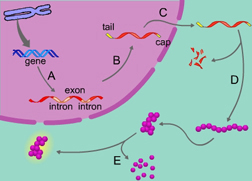
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
RNA processing is indicated by the letter _____. (Activity: Overview: Control of Gene Expression) 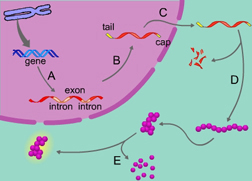
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
Which of the following processes is NOT indicated by the label A, B, C, D, or E? (Activity: Overview: Control of Gene Expression) 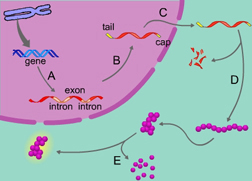
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
_____ bind(s) to DNA enhancer regions. (Activity: Control of Transcription)
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
Click on the diagram to view the animation. What is the event that IMMEDIATELY follows the last event of this animation? (Activity: Control of Transcription)
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
Which of these indicates an enhancer region? (Activity: Control of Transcription) 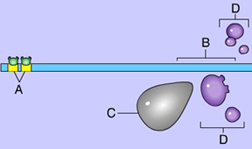
|
 |
| 16 . |
|
Which of these directly bind(s) to the promoter? (Activity: Control of Transcription) 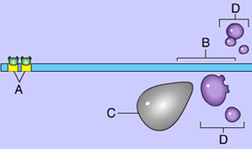
|
 |
| 17 . |
|
How can a single RNA transcript lead to the translation of different proteins? (Activity: Post-Transcriptional Control Mechanisms)
|
 |
| 18 . |
|
The mRNA region to which this regulatory protein is bound is called the _____. (Activity: Post-Transcriptional Control Mechanisms) 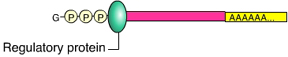
|
 |
| 19 . |
|
In the cytoplasm, the mRNA degradation begins at its _____. (Activity: Post-Transcriptional Control Mechanisms)
|
 |
| 20 . |
|
A poly-A tail's resistance to degradation is affected by the characteristics of the _____. (Activity: Post-Transcriptional Control Mechanisms)
|
 |
| 21 . |
|
Enzyme complexes that break down protein are called _____. (Activity: Post-Transcriptional Control Mechanisms)
|
 |
| 22 . |
|
The nuclear membrane's role in the regulation of gene expression involves _____. (Activity: Review: Control of Gene Expression)
|
 |
| 23 . |
|
What is the function of a spliceosome? (Activity: Review: Control of Gene Expression)
|
 |
| 24 . |
|
Protein-phosphorylating enzymes' role in the regulation of gene expression involves _____. (Activity: Review: Control of Gene Expression)
|
 |
| 25 . |
|
_____ is a carcinogen that promotes colon cancer. (Activity: Causes of Cancer)
|
 |
|