 |
| 1 . |
|
This is an image of a _____. (Activity: The Hershey-Chase Experiment) 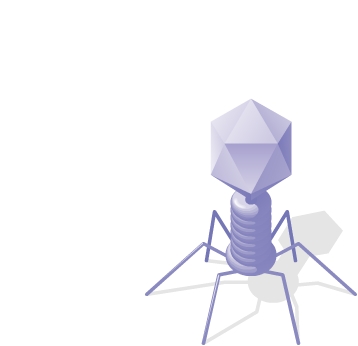
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
Who demonstrated that DNA is the genetic material of the T2 phage? (Activity: The Hershey-Chase Experiment)
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
The radioactive isotope 32P labels the T2 phage's _____. (Activity: The Hershey-Chase Experiment)
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
Hershey and Chase used _____ to radioactively label the T2 phage's proteins. (Activity: The Hershey-Chase Experiment)
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
After allowing phages grown with bacteria in a medium that contained 32P and 35S, Hershey and Chase used a centrifuge to separate the phage ghosts from the infected cell. They then examined the infected cells and found that they contained _____, which demonstrated that _____ is the phage's genetic material. (Activity: The Hershey-Chase Experiment)
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
In the accompanying image, a nucleotide is indicated by the letter _____. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure) 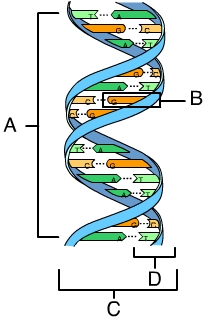
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
Which of these is a difference between a DNA and an RNA molecule? (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure)
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
This is an image of a(n) _____. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure) 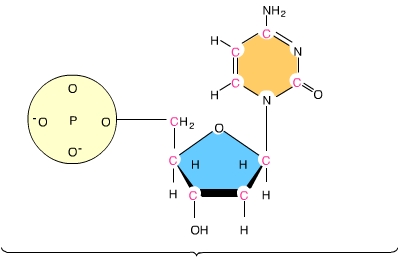
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
The letter A indicates a _____. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure) 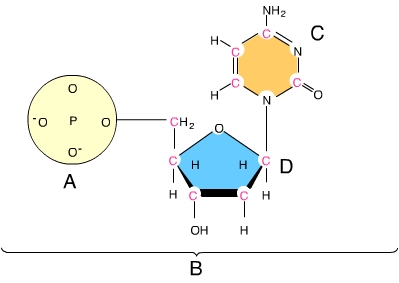
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
A nitrogenous base is indicated by the letter _____. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure) 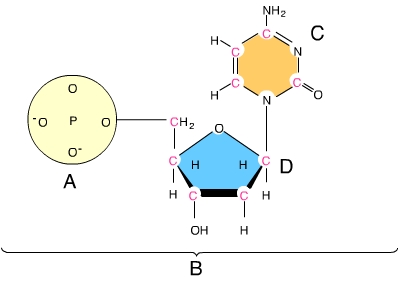
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
You can tell that this is an image of a DNA nucleotide and not an RNA nucleotide because you see a _____. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure) 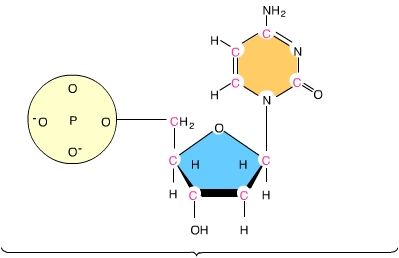
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
Which of these nitrogenous bases is found in DNA but not in RNA? (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure)
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
Which of these is(are) pyrimidines? (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure) 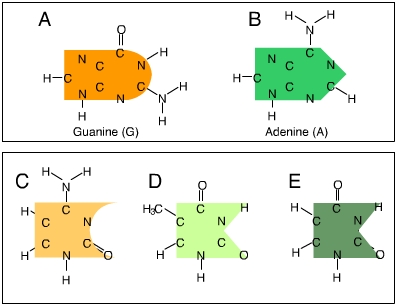
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
In a nucleotide, the nitrogenous base is attached to the sugar's _____ carbon and the phosphate group is attached to the sugar's _____ carbon. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure)
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
Nucleic acids are assembled in the _____ direction. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure)
|
 |
| 16 . |
|
In a DNA double helix an adenine of one strand always pairs with a(n) _____ of the complementary strand, and a guanine of one strand always pairs with a(n) _____ of the complementary strand. (Activity: DNA and RNA Structure),(Activity: DNA Double Helix), ( Activity: DNA Replication: A Closer Look)
|
 |
| 17 . |
|
Short segments of newly synthesized DNA are joined into a continuous strand by _____. (Activity: DNA Replication: An Overview), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
|
 |
| 18 . |
|
After DNA replication is completed, _____. (Activity: DNA Replication: An Overview), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Closer Look), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
|
 |
| 19 . |
|
The first step in the replication of DNA is catalyzed by _____. (Activity: DNA Replication: A Closer Look), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
|
 |
| 20 . |
|
The action of helicase creates _____. (Activity: DNA Replication: An Overview), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Closer Look), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
|
 |
| 21 . |
|
Why is the new DNA strand complementary to the 3' to 5' strands assembled in short segments? (Activity: DNA Replication: An Overview), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Closer Look), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
|
 |
| 22 . |
|
The synthesis of a new strand begins with the synthesis of a(n) _____. (Activity: DNA Replication: A Closer Look), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
|
 |
| 23 . |
|
Which of these is responsible for catalyzing the formation of an RNA primer? (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
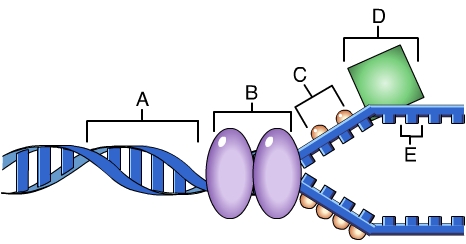
|
 |
| 24 . |
|
An old DNA strand is used as a _____ for the assembly of a new DNA strand. (Activity: DNA Replication: An Overview), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Closer Look), (Activity: DNA Replication: A Review)
|
 |
|