 |
| 1 . |
|
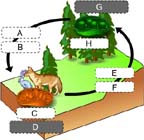
What process occurs in structure H? (Activity: Build a Chemical Cycling System)
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
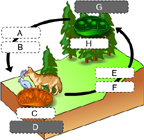
What molecules belong in space A and B? (Activity: Build a Chemical Cycling System)
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
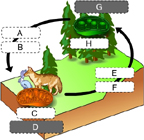
What organelle is indicated by the letter C? (Activity: Build a Chemical Cycling System)
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
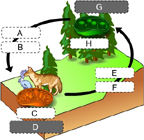
What molecules belong in spaces E and F? (Activity: Build a Chemical Cycling System)
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
What process occurs in Box A? (Activity: Overview of Cellular Respiration)
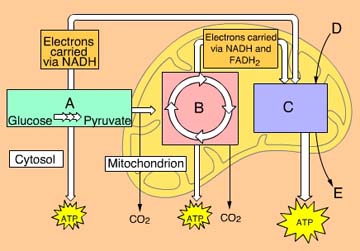
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
What process occurs within Box B? (Activity: Overview of Cellular Respiration)
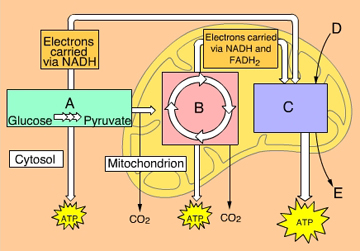
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
What molecule is indicated by the letter D? (Activity: Overview of Cellular Respiration)
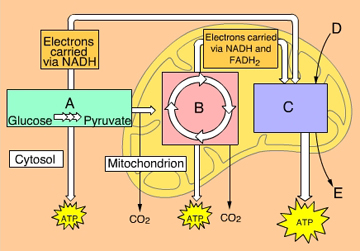
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
How many NADH are produced by glycolysis? (Activity: Glycolysis)
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
In glycolysis, ATP molecules are produced by _____. (Activity: Glycolysis)
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
Which of these is NOT a product of glycolysis? (Activity: Glycolysis)
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
In glycolysis, what starts the process of glucose oxidation? (Activity: Glycolysis)
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
In glycolysis there is a net gain of _____ ATP. (Activity: Glycolysis)
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
Which of these enters the citric acid cycle? (Activity: The Citric Acid Cycle)
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
How does pyruvate enter a mitochondrion? (Activity: The Citric Acid Cycle)
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
In the citric acid cycle, ATP molecules are produced by _____. (Activity: The Citric Acid Cycle)
|
 |
| 16 . |
|
Which of these is NOT a product of the citric acid cycle? (Activity: The Citric Acid Cycle)
|
 |
| 17 . |
|
For each glucose that enters glycolysis, _____ acetyl CoA enter the citric acid cycle. (Activity: Electron Transport)
|
 |
| 18 . |
|
For each glucose that enters glycolysis, _____ NADH + H+ are produced by the citric acid cycle. (Activity: Electron Transport)
|
 |
| 19 . |
|
In cellular respiration, most ATP molecules are produced by _____. (Activity: Electron Transport)
|
 |
| 20 . |
|
The final electron acceptor of cellular respiration is _____. (Activity: Electron Transport)
|
 |
| 21 . |
|
During electron transport, energy from _____ is used to pump hydrogen ions into the _____. (Activity: Electron Transport)
|
 |
| 22 . |
|
Structure A is _____. (Activity: Electron Transport)
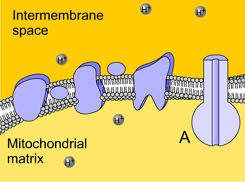
|
 |
| 23 . |
|
The proximate (immediate) source of energy for oxidative phosphorylation is _____. (Activity: Electron Transport)
|
 |
| 24 . |
|
In muscle cells, fermentation produces _____. (Activity: Fermentation)
| | pyruvate |
| | carbon dioxide, ethanol, NAD+, and ATP |
| | carbon dioxide, ethanol, NADH, and ATP |
| | carbon dioxide, lactate, NAD+, and ATP |
| | carbon dioxide, lactate, NADH, and ATP |
|
 |
| 25 . |
|
In fermentation _____ is reduced and _____ is oxidized. (Activity: Fermentation)
|
 |
|