 |
| 1 . |
|
Which of these is a receptor molecule? (Activity: Overview of Cell Signaling) 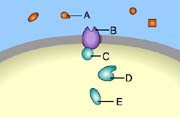
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
A signal transduction pathway is initiated when a _____ binds to a receptor. (Activity: Overview of Cell Signaling)
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
Which of these is a signal molecule? (Activity: Overview of Cell Signaling) 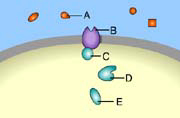
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
A signal molecule is also known as a(n) _____. (Activity: Overview of Cell Signaling)
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
Which of these receptors is NOT a membrane receptor? (Activity: Reception) 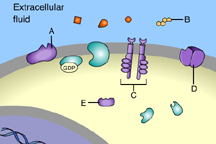
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
Which of these is a G-protein-linked receptor? (Activity: Reception) 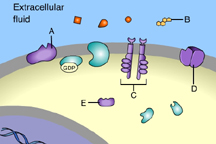
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
Which of these is a receptor tyrosine kinase? (Activity: Reception) 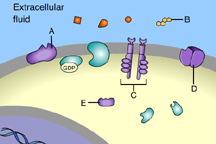
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
Which of these is an ion-channel receptor? (Activity: Reception) 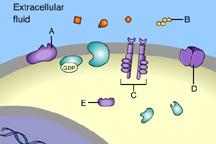
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
The binding of signal molecules to _____ results in the phosphorylation of tyrosines. (Activity: Reception) 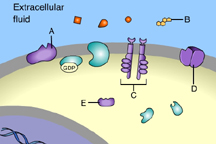
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
Which of these receptor molecules would allow Na+ to flow into the cell? (Activity: Reception) 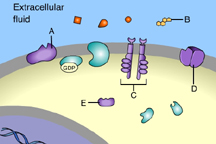
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
Which of these extracellular signal molecules could diffuse through a plasma membrane and bind to an intracellular receptor? (Activity: Reception)
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
A(n) _____ is an example of a signal molecule that can bind to an intracellular receptor and thereby cause a gene to be turned on or off. (Activity: Reception)
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
_____ is a signal molecule that binds to an intracellular receptor. (Activity: Reception) 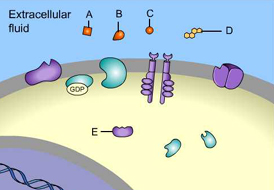
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
Thyroid hormones bind to _____ receptors. (Activity: Reception)
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
Which of these acts as a second messenger? (Activity: Signal Transduction Pathways) 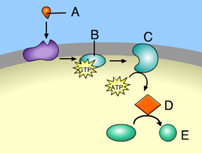
|
 |
| 16 . |
|
Which of these acts as a second messenger? (Activity: Signal Transduction Pathways)
|
 |
| 17 . |
|
Calcium ions that act as second messengers are stored in _____. (Activity: Signal Transduction Pathways)
|
 |
| 18 . |
|
_____ catalyzes the production of _____, which then opens an ion channel that releases _____ into the cell's cytoplasm. (Activity: Signal Transduction Pathways)
|
 |
| 19 . |
|
A protein kinase activating many other protein kinases is an example of _____. (Activity: Signal Transduction Pathways)
|
 |
| 20 . |
|
The cleavage of glycogen by glycogen phosphorylase releases _____. (Activity: Cellular Responses)
|
 |
| 21 . |
|
Epinephrine acts as a signal molecule that attaches to _____ proteins. (Activity: Cellular Responses)
|
 |
| 22 . |
|
Which of these is a receptor for calcium ions? (Activity: Cellular Responses)
|
 |
| 23 . |
|
Which of these is NOT correct? (Activity: Cellular Responses)
|
 |
| 24 . |
|
A toxin that inhibits the production of GTP would interfere with the function of a signal transduction pathway that is initiated by the binding of a signal molecule to _____ receptors. (Activity: Cellular Responses)
|
 |
| 25 . |
|
Which of these is a logical signal transduction pathway? (Activity: Build a Signaling Pathway)
| | A receptor tyrosine kinase activates adenylyl cyclase, which activates phospholipase C, which converts ATP into cyclic AMP, which binds to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. |
| | An ion-channel receptor opens, allowing a steroid hormone to enter the cell; the steroid hormone then activates protein kinases that convert GTP to GDP, which binds to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. |
| | An intracellular receptor activates phospholipase C, which cleaves a membrane protein to form IP3, which then activates the opening of an ER channel protein, which releases cyclic AMP into the cytoplasm, where it binds to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. |
| | A G-protein-linked receptor activates G protein, which activates phospholipase C, which cleaves a membrane protein to form IP3, which binds to a calcium channel on the ER, which opens to release calcium ions into the cytoplasm, which bind to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. |
|
 |
|