 |
| 1 . |
|
The result of the following cross indicates the orange eyes are _____ black eyes. (Activity 9A) 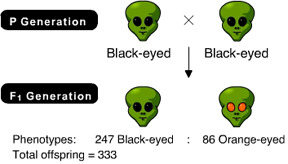
|
 |
| 2 . |
|
If O represents the allele for black eyes (dominant) and o represents the allele for orange eyes (recessive), what would be the genotypic ratio of a cross between a heterozygous black-eyed MendAlien and an orange-eyed MendAlien? (Activity 9A)
|
 |
| 3 . |
|
If O represents the allele for black eyes (dominant) and o represents the allele for orange eyes (recessive), what would be the phenotypic ratio of a cross between a heterozygous black-eyed MendAlien and an orange-eyed MendAlien? (Activity 9A)
|
 |
| 4 . |
|
The result of the following cross indicates that the genotype of the female parent is _____. (Activity 9A) 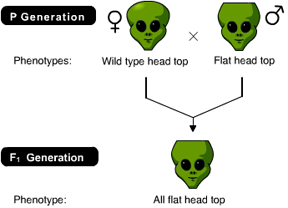
|
 |
| 5 . |
|
The result of the following cross indicates that the genotype of the male parent is _____. (Activity 9A) 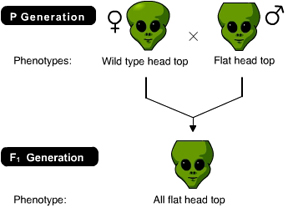
|
 |
| 6 . |
|
The result of the following cross indicates that genotypically the offspring _____. (Activity 9A) 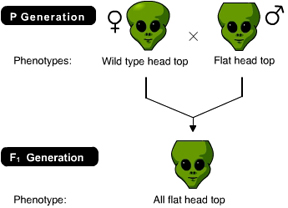
|
 |
| 7 . |
|
Which of these is a testcross? (Activity 9A)
|
 |
| 8 . |
|
That each gamete contains a single allele of the eye color gene is an illustration of _____. (Activity 9A) 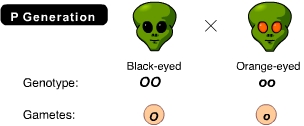
|
 |
| 9 . |
|
What is the genotype of the parent with orange eyes and white skin? (Note: orange eyes are recessive.) (Activity 9B) 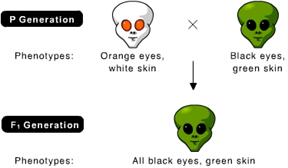
|
 |
| 10 . |
|
What is the genotype of the offspring? (Activity 9B) 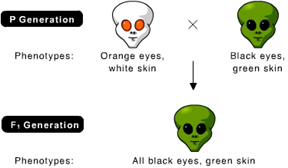
|
 |
| 11 . |
|
In order to determine the genotype of a MendAlien with black eyes and green skin, you would cross this individual with a(n) _____ individual. (Activity 9B)
|
 |
| 12 . |
|
Black eyes are dominant to orange eyes, and green skin is dominant to white skin. Sam, a MendAlien with black eyes and green skin, has a parent with orange eyes and white skin. Carole is a MendAlien with orange eyes and white skin. If Sam and Carole were to mate, the predicted phenotypic ratio of their offspring would be _____. (Activity 9B)
| | 1black eyes, green skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin |
| | 3 black eyes, green skin : 3 black eyes, white skin : 9 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin |
| | 1 black eyes, green skin : 3 black eyes, white skin : 3 orange eyes, green skin : 9 orange eyes, white skin |
| | 9 black eyes, green skin : 3 black eyes, white skin : 3 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin |
| | There is insufficient information to determine Sam's genotype. |
|
 |
| 13 . |
|
A cross between an individual with orange eyes and green skin and an individual with black eyes and white skin is an example of a _____ cross. (Activity 9B)
|
 |
| 14 . |
|
A phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 in the offspring of a cross indicates that _____. (Activity 9B)
|
 |
| 15 . |
|
The observed distribution of alleles into gametes is an illustration of _____. (Activity 9B) 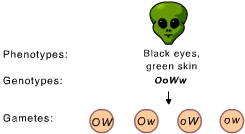
|
 |
| 16 . |
|
An individual heterozygous for eye color, skin color, and number of eyes mates with an individual who is homozygous recessive for all three characters; what would be the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? [Hint: O = black eyes, o = orange eyes; W = green skin, w = white skin; C = two eyes, c = one eye] (Activity 9B)
| | 9 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 3 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 3 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye : 9 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 3 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 3 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye |
| | 9 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 3 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 3 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye |
| | 1 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye |
| | 1 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye |
| | 9 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 9 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 9 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye |
|
 |
| 17 . |
|
A OoWw x ooww cross yields a phenotypic ratio of approximately 5 black eyes, green skin : 5 orange eyes, white skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin. Which of the following best explains these results? (Activity 9B)
|
 |
| 18 . |
|
In the following cross the genotype of the female parent is OoWw. What is the genotype of the male parent? [Hint: O = black eyes, o = orange eyes, W = green skin, w = white skin] (Activity 9B) 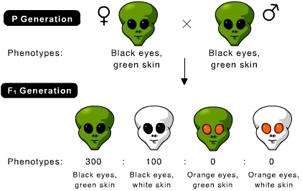
|
 |
| 19 . |
|
In a situation in which genes assort independently, what is the ratio of the gametes produced by an AaBB individual? (Activity 9B)
|
 |
| 20 . |
|
Mendel worked _____. (Activity 9C)
|
 |
| 21 . |
|
Andalusian chickens with the genotype CBCB are black, those with the genotype CWCW are white, and those with the genotype CBCW are gray. What is the relationship between the CB and CW alleles? (Activity 9D)
|
 |
| 22 . |
|
Andalusian chickens with the genotype CBCB are black, those with the genotype CWCW are white, and those with the genotype CBCW are gray. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of a CBCW x CBCW cross? (Activity 9D)
|
 |
| 23 . |
|
Andalusian chickens with the genotype CBCB are black, those with the genotype CWCW are white, and those with the genotype CBCW are gray. What is the expected genotypic ratio of a CBCW x CBCW cross? (Activity 9D)
|
 |
| 24 . |
|
Andalusian chickens with the genotype CBCB are black, those with the genotype CWCW are white, and those with the genotype CBCW are gray. What is the expected genotypic ratio of a CBCB x CBCW cross? (Activity 9D)
|
 |
| 25 . |
|
Andalusian chickens with the genotype CBCB are black, those with the genotype CWCW are white, and those with the genotype CBCW are gray. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of a CBCB x CBCW cross? (Activity 9D)
|
 |
| 26 . |
|
Based on the results of this cross, you determine that _____. (Activity 9E) 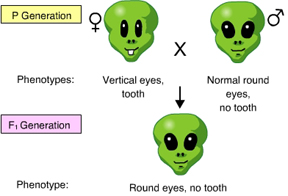
|
 |
| 27 . |
|
The results of the following cross indicate that the _____. (Activity 9E) 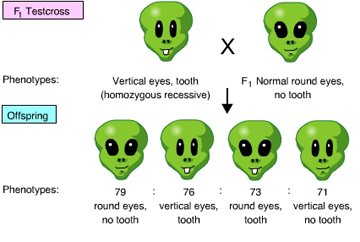
|
 |
| 28 . |
|
An F1 individual can produce _____ different gametes when both eye and tooth genes are considered. (Activity 9E) 
|
 |
| 29 . |
|
Given these chromosomes, which of the choices represents the possible recombinant gametes? (Activity 9E) 
|
 |
| 30 . |
|
The results of a F1 testcross are: 250 bald head, four ears : 247 hairy head, six ears : 21 bald head, six ears : 19 hairy head, four ears. How many map units apart are the head and ear genes? (Activity 9E)
|
 |
| 31 . |
|
Which of the individuals is homozygous recessive for both of the gene pairs? (Activity 9E) 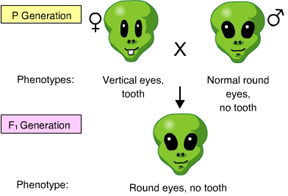
|
 |
| 32 . |
|
The results of the following cross indicate that the _____. (Activity 9E) 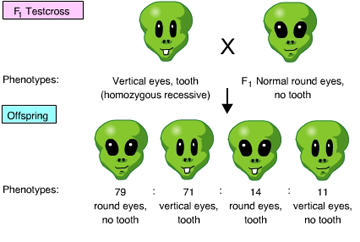
|
 |
| 33 . |
|
The recombination frequency between gene A and gene B is 8.4%, the recombination frequency between gene A and gene C is 6.8%, and the recombination frequency between gene B and gene C is 15.2%. Which of these is the correct arrangement of these genes? (Activity 9E)
|
 |
| 34 . |
|
A color-blind woman mates with a male with normal color vision. Which of these results would indicate that color blindness is caused by an X-linked recessive allele? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 35 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind man has a daughter with normal color vision. What is the genotype of the daughter? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 36 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind man has a daughter with normal color vision. She mates with a male who has normal color vision. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 37 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind man has a daughter with normal color vision. She mates with a color-blind male. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 38 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A woman who is homozygous for normal color vision mates with a color-blind male. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 39 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind woman mates with a male with normal color vision. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 40 . |
|
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. Under what conditions can an unaffected male have a color-blind daughter? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 41 . |
|
Hypophosphatemia (vitamin D–resistant rickets) is inherited as an X-linked dominant. An unaffected woman mates with a male with hypophosphatemia. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 42 . |
|
Hypophosphatemia (vitamin D–resistant rickets) is inherited as an X-linked dominant. A woman without hypophosphatemia and a man with hypophosphatemia have a daughter. The daughter mates with a male without hypophosphatemia. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
| 43 . |
|
Suppose that having three nostrils is a Y-linked character. A woman with two nostrils mates with a man with three nostrils. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? (Activity 9F)
|
 |
|